Love Canal Disaster
By: Olivia Farinas

"The Love Canal landfill contained approximately 21,800 tons of chemical wastes. Substantial migration and contamination of soil, groundwater and basement air of nearby homes was apparent in the late 1970s."
-Epidemiology Journal
Love Canal was infested with toxins and wastes that not only harmed human health, but also destroyed the environment around it. This is a perfect example of groundwater pollution, which is something we learned in our class! Specifically, the types of pollutants included water-soluble inorganic materials that were acids, salts, and other toxic metals and organic chemicals as well.
Chemicals found in homes in Love Canal
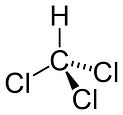
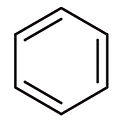

chloroform benzene trichloroethene


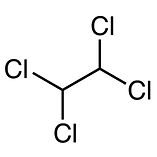
toluene chlorobenzene tetrachloroethene



chlorotoluene
trichlorobenzene
Environmental Impacts of Chemicals
For example, benzene has been known to react with other chemicals to create smog. Toluene can cause membrane damage in plants. When it rains/snows, which when it did in Love Canal, these chemicals can be carried through into the groundwater and create contamination. Aquatic life can be affected from this tremendously, resulting in infertility.


Wildlife Impacts
Animals that live near Love Canal were studied by a John J. Christian of SUNY Binghamton during the 80s, a few years after evacuation occurred. spe
Specifically, he looked at voles, which are rodents, that lived near the fenced-off area and had a life expectancy of around 54 days. These voles tended to have damaged livers, excess fat, premature reproductive organs, and low amounts of glycogen. It is unknown as to what chemical causes this outcome. On the other hand, those who lived further away lived 100 days after their first month, which was the normal life span.
Additionally, dioxin concentrations were taken from multiple fish species across different rivers and creeks near Love Canal. The tables below display the high amounts of different types of dioxins found in the fish species. These emphasize the intense effects that most people may not realize.


Cleanup Process


To learn more about the cleanup activities for Love Canal:
Cleanup activities are laid out by the EPA:
References
Benzene. National Pollutant Inventory. (n.d.). Retrieved April 23, 2022, from http://www.npi.gov.au/resource/benzene#:~:text=What%20effect%20does%20benzene%20have,to%20contaminate%20water%20and%20soil.
Department of Health. Love Canal - Public Health Time Bomb. (n.d.). Retrieved April 23, 2022, from https://www.health.ny.gov/environmental/investigations/love_canal/lctimbmb.htm\
Dioxins and Furans in Fish Below Love Canal, NY. (1993, August). Retrieved April 23, 2022, from https://www.dec.ny.gov/docs/fish_marine_pdf/lovecanalrpt.pdf
Engelhaupt, E. (2008, November 17). Happy Birthday, Love Canal. Chemical and Engineering News. Retrieved April 23, 2022, from https://cen.acs.org/articles/86/i46/Happy-Birthday-Love-Canal.html
Hilts, P. J. (1983, October 3). Study says chemicals in Love Canal are killing nearby animals. The Washington Post. Retrieved April 23, 2022, from https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/politics/1983/10/03/study-says-chemicals-in-love-canal-are-killing-nearby-animals/7dbc604c-e871-4147-9735-fa86d81b7efe/
Houghton, W. (1879). Carassius auratus. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved April 23, 2022, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Carassius_auratus.jpg.
Love Canal: Case study in contamination. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VrWtd1P-NoU
MilliporeSigma | United States. (n.d.). Retrieved April 23, 2022, from https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
The continuing impact of Love Canal. (2000). Epidemiology, 11(4). https://doi.org/10.1097/00001648-200007000-00399
Toluene. National Pollutant Inventory. (n.d.) Retrieved April 23, 2022, from http://www.npi.gov.au/resource/toluene-methylbenzene#:~:text=Toluene%20has%20caused%20membrane%20damage,is%20expected%20to%20minimally%20bioaccumulate.